The 74×245 (ex 74HC245) is a chip designed as an octal bus transceiver with 3-state outputs, allowing for bidirectional data transmission between different parts of a digital system.
In this guide, you’ll learn the things you need to know about this chip in order to use bus transceivers effectively in your own projects.
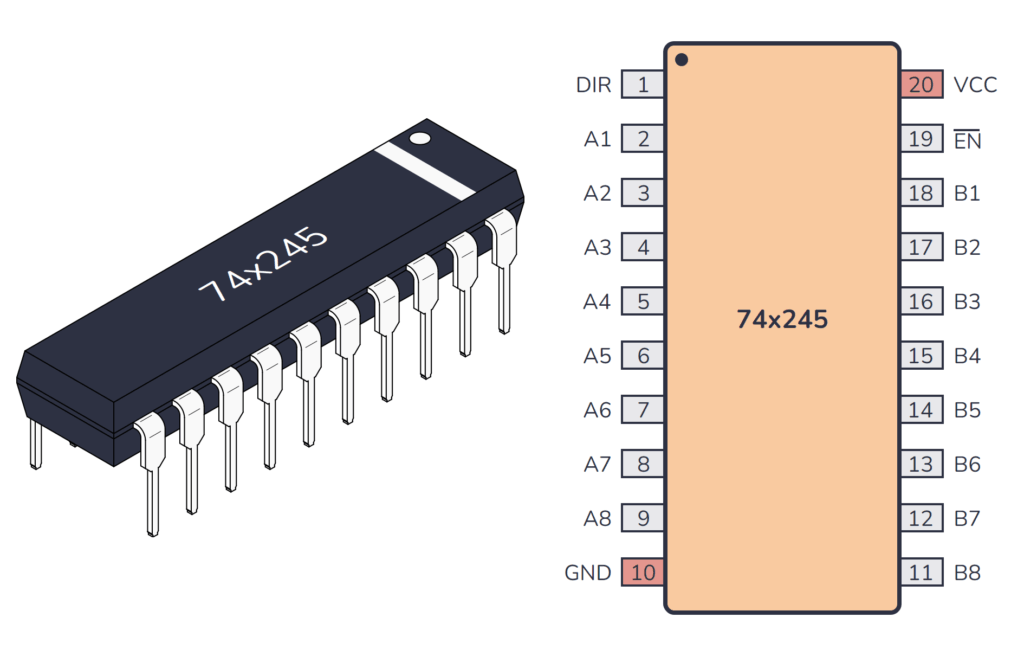
What does the 74HC245 / 74LS245 do?
The 74×245 is a bidirectional bus transceiver. It helps data flow between two separate buses, enabling communication in both directions. The chip has 8 data lines that connect each bus on either side of the chip.
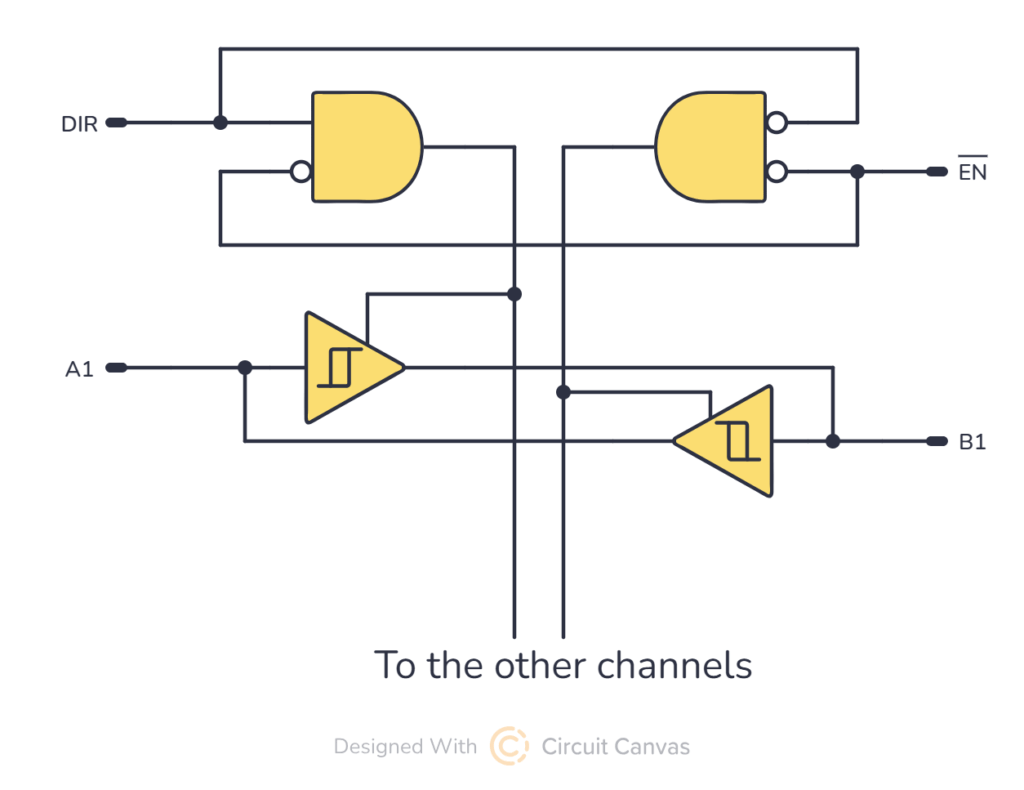
The 74×245 is useful when you need to manage data flow and prevent conflicts in systems like microprocessors and memory circuits.
How To Use This Chip
You control the direction of data flow with the direction (DIR) input. When you set DIR to HIGH, data moves from bus A to bus B. And when you set DIR to LOW, data travels from bus B to bus A.
You can enable/disable the outputs using the enable (EN) input.
When this pin is LOW, the transceiver works to transfer data. If it is HIGH, the buses are disconnected, so that both sides goes into a high-impedance state. This high-impedance state helps prevent interference with other devices on the same bus.
Voltage and Current
The 74HC245 comes in a 20-pin package, and you need to connect it to power before you can use it. Most 7400 ICs support a VCC voltage of 5V.
Get the 555 Timer Cheatsheet
A super helpful reference that makes it easy to design circuits, so that you can build oscillators, timer circuits, and more in no time.
One difference between the HC and LS version of the chip is that the 74HC245 supports 2V to 6V, while the 74LS245 only supports 5V.
The 74HC version of this chip can normally supply a maximum of 8 mA from an output pin. If you’re using the 74LS version, the maximum current you can pull out of one output pin is 15 mA when the pin is high (sourcing) or 24 mA when the pin is low (sinking).
But these values can differ between models, so check the datasheet of your model to verify.
74×245 Pinout
The 74×245 has 20 pins and contains Enable and direction pins control output enables laid out as shown in the pinout diagram below:
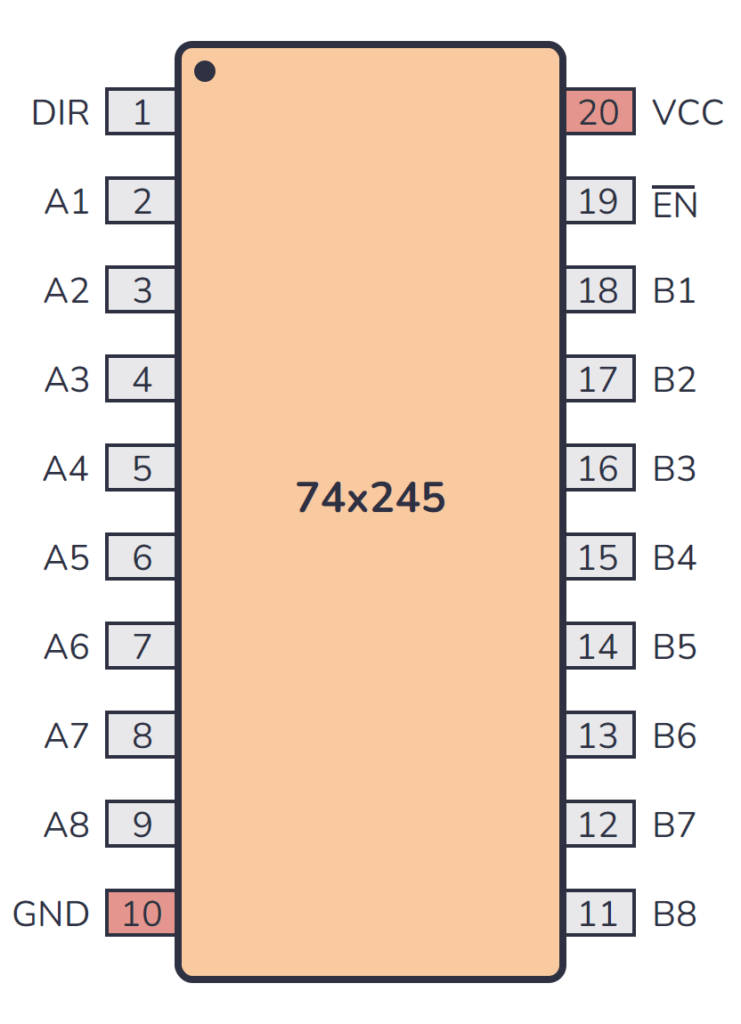
| Pin Name | Pin # | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIR | 1 | Input | Determines data flow direction: A to B when high, B to A when low. |
| A1 | 2 | Input/Output | Data bus line A1. |
| A2 | 3 | Input/Output | Data bus line A2. |
| A3 | 4 | Input/Output | Data bus line A3. |
| A4 | 5 | Input/Output | Data bus line A4. |
| A5 | 6 | Input/Output | Data bus line A5. |
| A6 | 7 | Input/Output | Data bus line A6. |
| A7 | 8 | Input/Output | Data bus line A7. |
| A8 | 9 | Input/Output | Data bus line A8. |
| GND | 10 | Power | Connect to ground (GND). |
| B8 | 11 | Input/Output | Data bus line B8. |
| B7 | 12 | Input/Output | Data bus line B7. |
| B6 | 13 | Input/Output | Data bus line B6. |
| B5 | 14 | Input/Output | Data bus line B5. |
| B4 | 15 | Input/Output | Data bus line B4. |
| B3 | 16 | Input/Output | Data bus line B3. |
| B2 | 17 | Input/Output | Data bus line B2. |
| B1 | 18 | Input/Output | Data bus line B1. |
| EN | 19 | Input | Output enable input (active low). Enables the transceivers when low. |
| VCC | 20 | Power | Positive power supply. Connect to +5V power. |
Alternatives and Equivalents for 74HC245 / 74LS245
There are many versions of the 74×245 chip. They all have the same functionality, but with different specifications such as supported voltages and maximum current output.
Here’s a list of a few equivalents of this chip:
- 74HC245 (High-speed CMOS)
- 74HCT245 (High-speed CMOS, TTL compatible)
- 74LS245 (High-speed TTL)
- 74LVC245 (Low Voltage TTL)
- 74AC245 (Advanced CMOS)
- 74ALS245 (Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL)
- 74F245 (Very High Speed)
- 74C245 (CMOS, similar to the 4000-series)
Some manufacturers also add a prefix, such as the SN74HC245 and SN74LS245 by Texas Instruments.
Can’t find the 74×245 anywhere? Then try one of the following IC alternatives:
- 74×240 – Octal buffer/line driver with inverting outputs.
- 74×241 – Octal buffer/line driver with non-inverting outputs.
- 74×244 – Octal buffer/line driver with non-inverting outputs.
- 74×540 – Octal buffer/line driver with inverting outputs.
- 74×541 – Octal buffer/line driver with non-inverting outputs.
- CD4503 – Hex non-inverting buffer with 3-state outputs.
If you can’t find the 74×245 IC in your local electronics store, don’t worry, you’ll most likely find it in one of the stores listed on this page of online stores where you’ll find components and tools for all your electronics projects.
Datasheet for the 74LS245 and 74HC245 chips
Download the PDF datasheet for your version of the 74×245 here:
- SN74HC245 (Texas Instruments)
- SN74LS245 (Texas Instruments)
- 74HC245 (Futurlec)
- 74LS245 (Futurlec)
- 74HC245 (Nexperia)

Get the 555 Timer Cheatsheet
A super helpful reference that makes it easy to design circuits, so that you can build oscillators, timer circuits, and more in no time.