The 74×47 (ex 74LS47) is a chip that converts BCD (Binary-Coded Decimal) to signals for controlling a 7-segment display, which can be useful in creating digital readouts from binary data.
It’s designed to use with common anode displays. If you need common cathode, check out 74LS48 instead.
In this guide, you’ll learn the things you need to know about this chip in order to use BCD to 7-segment display decoding in your own projects.
What does the 74HC47 / 74LS47 do?
The 74×47 is a Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) to 7-segment display driver. It takes a 4-bit BCD input (which represents numbers 0 to 9) and converts it into signals that can light up the appropriate segments on a 7-segment display to show the equivalent decimal digit.
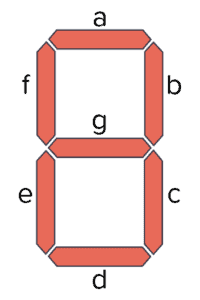
Here’s how it works:
- You provide a BCD input, and the chip will turn on the specific segments required to display the corresponding decimal digit.
- It has outputs connected to the segments (a to g) of the display.
- It also has features like ripple blanking, which turns off the display when not in use, and a lamp test, which lights up all segments for checking.
This chip is handy for creating digital clocks, calculators, and any device requiring a numerical display.
How To Use This Chip
The 74HC47 comes in a 16-pin package, and you need to connect it to power before you can use it. Most 7400 ICs support a VCC voltage of 5V. One difference between the HC and LS version of the chip is that the 74HC47 supports 2V to 6V, while the 74LS47 only supports 5V.
This chip uses open-collector outputs that can drive the segments directly. Just use a resistor in series to limit the current.
Build Something Useful This Evening
This gadget lets you use any IR remote-control to control your lamp, garden lights, heater oven, garage door, or anything else.
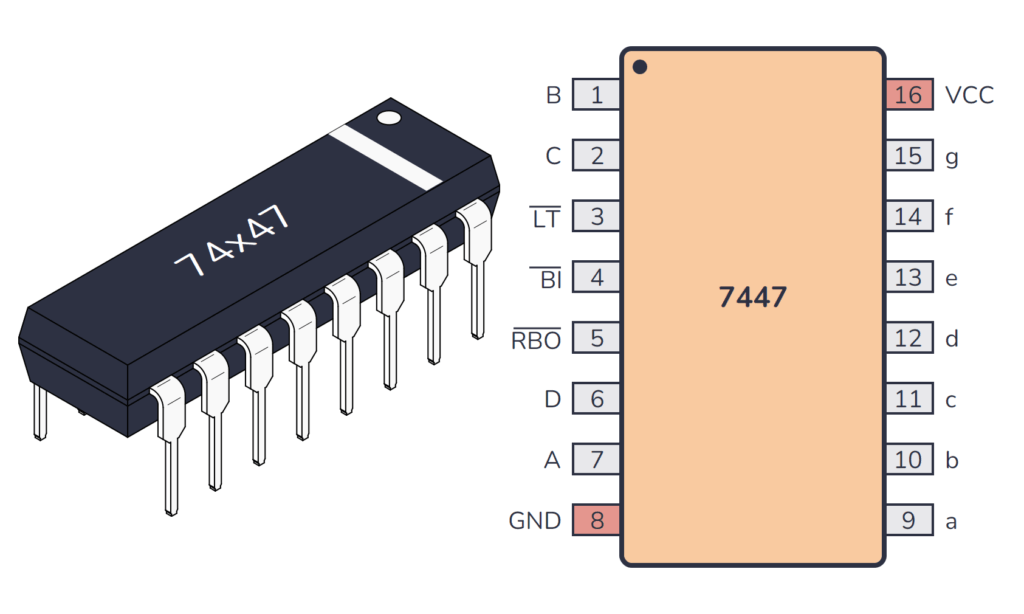
74×47 Pinout
The 74×47 has 16 pins and contains BCD to 7-segment (common anode) decoder/driver with active low outputs laid out as shown in the pinout diagram below:
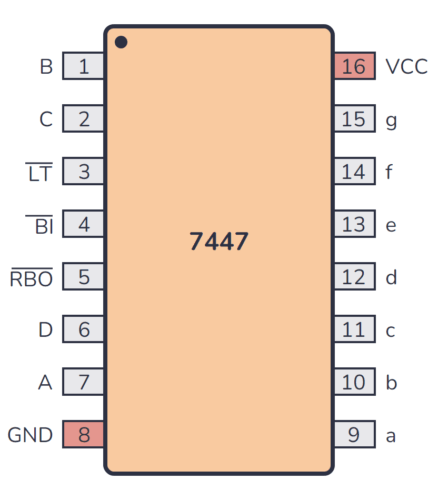
| Pin Name | Pin # | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 1 | Input | Binary input for the BCD decoder. |
| C | 2 | Input | Binary input for the BCD decoder. |
| LT | 3 | Input | Lamp test input (active low). |
| BI | 4 | Input | Blanking input (active low). |
| RBO | 5 | Output | Ripple blanking output (active low). |
| D | 6 | Input | Binary input for the BCD decoder. |
| A | 7 | Input | Binary input for the BCD decoder. |
| GND | 8 | Power | Connect to ground (GND). |
| a | 9 | Output | Segment output ‘a’. |
| b | 10 | Output | Segment output ‘b’. |
| c | 11 | Output | Segment output ‘c’. |
| d | 12 | Output | Segment output ‘d’. |
| e | 13 | Output | Segment output ‘e’. |
| f | 14 | Output | Segment output ‘f’. |
| g | 15 | Output | Segment output ‘g’. |
| VCC | 16 | Power | Positive power supply. Connect to +5V power. |
Alternatives and Equivalents for 74HC47 / 74LS47
There are many versions of the 74×47 chip. They all have the same functionality, but with different specifications such as supported voltages and maximum current output.
Here’s a list of a few equivalents of this chip:
- 74HC47 (High-speed CMOS)
- 74HCT47 (High-speed CMOS, TTL compatible)
- 74LS47 (High-speed TTL)
- 74LVC47 (Low Voltage TTL)
- 74AC47 (Advanced CMOS)
- 74ALS47 (Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL)
- 74F47 (Very High Speed)
- 74C47 (CMOS, similar to the 4000-series)
Some manufacturers also add a prefix, such as the SN74HC47 and SN74LS47 by Texas Instruments.
Can’t find the 74×47 anywhere? Then try one of the following IC alternatives:
- 74×48 – BCD to 7-segment display decoder/driver.
- 74×49 – BCD to 7-segment display decoder/driver.
- 74×145 – BCD to decimal decoder/driver.
- 74×247 – BCD to 7-segment display decoder/driver (with open-collector outputs).
- CD4511 – BCD to 7-segment display decoder/driver.
If you can’t find the 74×47 IC in your local electronics store, don’t worry, you’ll most likely find it in one of the stores listed on this page of online stores where you’ll find components and tools for all your electronics projects.
Datasheet for the 74LS47 and 74HC47 chips
Download the PDF datasheet for your version of the 74×47 here:
Get the 555 Timer Cheatsheet
A super helpful reference that makes it easy to design circuits, so that you can build oscillators, timer circuits, and more in no time.