The 74×42 (ex 74HC42) is a chip with a BCD to decimal decoder, also called a 1-of-10 decoder that takes a 4-bit input signal and turns 1 out of 10 outputs high.
In this guide, you’ll learn the things you need to know about this chip in order to use this type of decoder in your own projects.
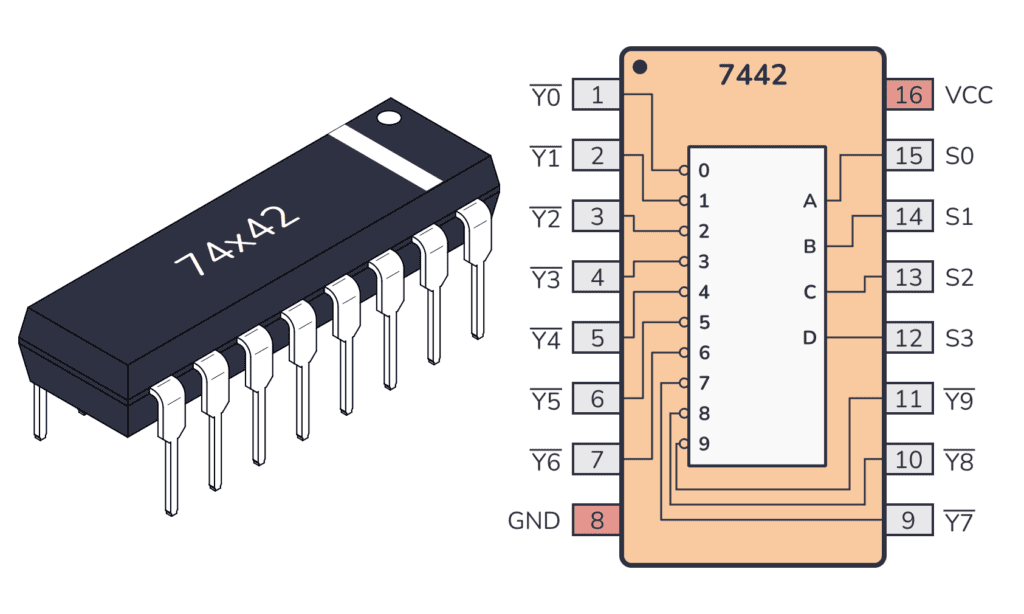
What does the 74HC42 / 74LS42 do?
This 74×42 chip takes four Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) inputs, ranging from S0 to S3. It outputs one of ten mutually exclusive outputs, Y0 to Y9. The design guarantees that if the input represents a decimal number greater than nine, all outputs will be HIGH.
While it’s designed for BCD to decimal (1-in-10) decoding, it can function as a 1-of-8 decoder by using the most significant input bit (S3) as an enable/disable input.
- When S3 is LOW, the chip acts as a 1-in-8 decoder using inputs S0-S2.
- When S3 is HIGH, all outputs are disabled, effectively turning it off.
However, a dedicated 1-in-8 decoder like the 74HC138 might be a more efficient choice in terms of pin count and simplicity.
How To Use This Chip
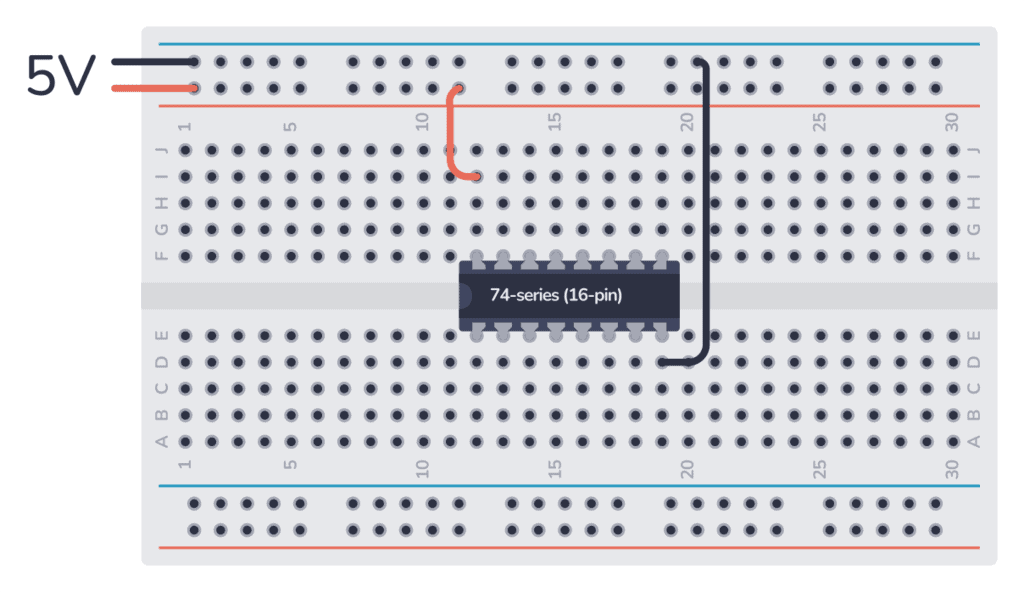
The 74HC42 comes in a 16-pin package, and you need to connect it to power before you can use it. Most 7400 ICs support a VCC voltage of 5V. One difference between the HC and LS version of the chip is that the 74HC42 supports 2V to 6V, while the 74LS42 only supports 5V.
The maximum current you can pull out of one output pin is 4 mA when the pin is high (sourcing) or 8/16 mA when the pin is low (sinking). This can differ between models, so check the datasheet of your model to verify.
Once you’ve connected it to power, you can use any of the 1-of-10 inverting decoder/demultiplexer inside.

10 Simple Steps to Learn Electronics
Electronics is easy when you know what to focus on and what to ignore. Learn what "the basics" really is and how to learn it fast.
74×42 Pinout
The 74×42 has 16 pins and contains BCD to decimal decoder as shown in the pinout diagram below:
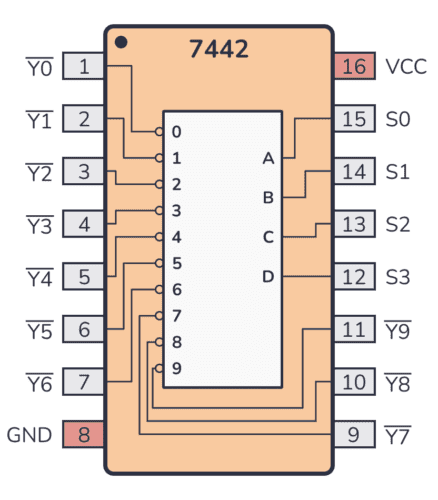
| Pin Name | Pin # | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y0 | 1 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| Y1 | 2 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| Y2 | 3 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| Y3 | 4 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| Y4 | 5 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| Y5 | 6 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| Y6 | 7 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| GND | 8 | Power | Connect to ground (GND). |
| Y7 | 9 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| Y8 | 10 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| Y9 | 11 | Output | Output from the multiplexer (inverted). |
| S3 | 12 | Input | Control signal that controls the multiplexer. |
| S2 | 13 | Input | Control signal that controls the multiplexer. |
| S1 | 14 | Input | Control signal that controls the multiplexer. |
| S0 | 15 | Input | Control signal that controls the multiplexer. |
| VCC | 16 | Power | Positive power supply (VCC). Connect to +5V power. |
Alternatives and Equivalents for 74HC42 / 74LS42
There are many versions of the 74×42 chip. They all have the same functionality, but with different specifications such as supported voltages and maximum current output.
Here’s a list of a few equivalents of this chip:
- 74HC42 (High-speed CMOS)
- 74HCT42 (High-speed CMOS, TTL compatible)
- 74LS42 (High-speed TTL)
- 74LVC42 (Low Voltage TTL)
- 74AC42 (Advanced CMOS)
- 74ALS42 (Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL)
- 74F42 (Very High Speed)
- 74C42 (CMOS, similar to the 4000-series)
Some manufacturers also add a prefix, such as the SN74HC42 and SN74LS42 by Texas Instruments.
Can’t find the 74×42 anywhere? Then try one of the following IC alternatives:
- 74×138 – 3-to-8 decoder/demultiplexer
If you can’t find the 74×42 IC in your local electronics store, don’t worry, you’ll most likely find it in one of the stores listed on this page of online stores where you’ll find components and tools for all your electronics projects.
Datasheet for the 74LS42 and 74HC42 chips
Download the PDF datasheet for your version of the 74×42 here:

10 Simple Steps to Learn Electronics
Electronics is easy when you know what to focus on and what to ignore. Learn what "the basics" really is and how to learn it fast.