In this episode, we start out with the idea of building a buck converter with a microcontroller. We realize that we’ve never built a buck converter before, so we go through our thought process live to figure out what we need to do.
We built one buck converter each. Elias used a Bluepill and Oyvind used an Arduino. Then we talk about the process and what we learned during the build.
Listen to the Podcast
Show Notes
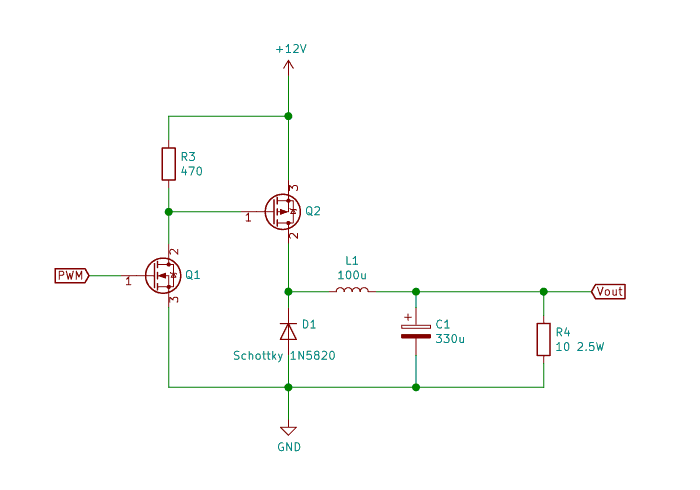
The buck converter circuit diagram Oyvind ended up with:
The Arduino Code Oyvind used:
#define PIN_INPUT A5
#define PIN_OUTPUT 9
int pwm_val = 10;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// PWM frequency:
TCCR1B = TCCR1B & B11111000 | B00000001; // 31372.55 Hz
//TCCR1B = TCCR1B & B11111000 | B00000010; // 3921.16 Hz
//TCCR1B = TCCR1B & B11111000 | B00000011; // 490.20 Hz (The DEFAULT)
//TCCR1B = TCCR1B & B11111000 | B00000100; // 122.55 Hz
//TCCR1B = TCCR1B & B11111000 | B00000101; // 30.64 Hz
}
void loop() {
double volt = getVoltage();
if (volt > 5.1)
pwm_val--;
else if (volt < 4.9)
pwm_val++;
if (pwm_val > 255)
pwm_val = 255;
if (pwm_val < 0)
pwm_val = 0;
analogWrite(PIN_OUTPUT, pwm_val);
Serial.print(volt);
Serial.print(" - Setting output to ");
Serial.println(pwm_val);
}
double getVoltage() {
int in = analogRead(PIN_INPUT);
double input_volt = 5.0 * in/1024;
//Serial.print("Input: ");
//Serial.println(input_volt);
return input_volt/0.18;
}More Podcast Tutorials

10 Simple Steps to Learn Electronics
Electronics is easy when you know what to focus on and what to ignore. Learn what "the basics" really is and how to learn it fast.
