Do you want to build a circuit that blinks a light? This inverter-based circuit is simple, and it’s small enough to fit on a breadboard.
The circuit uses standard basic electronic components and you can build it even if you have never built anything before. Check out the full build instructions in the video below:
Scroll down to find the complete circuit diagram, component list, and step-by-step instructions (in text-form) on how to build this circuit.
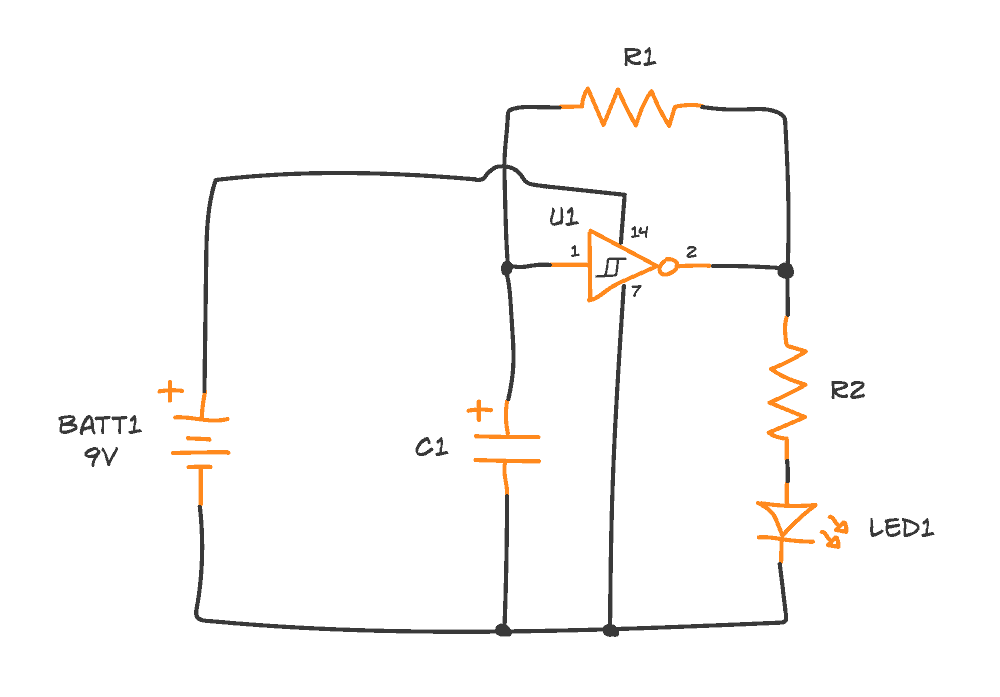
The Circuit Diagram
In the lessons, you learned that you needed an inverter for this circuit. But there’s one important point if you want to build this:
You need to use a Schmitt-triggered inverter. It’s an inverter where the voltage at which it switches from LOW to HIGH is higher than the voltage for switching from HIGH to LOW.
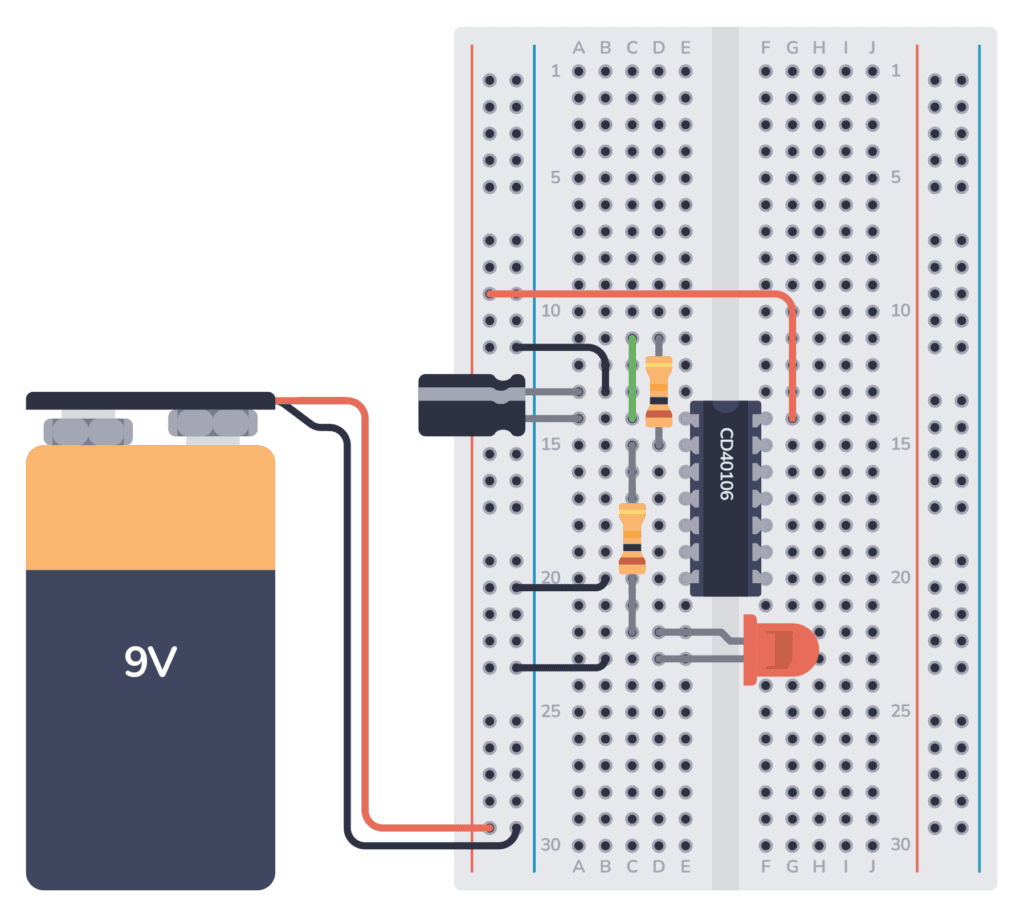
You’ll find the complete circuit diagram below.
The numbers next to each pin in the diagram represent the pin number on the integrated circuit. Click here for the pinout of the Hex Schmitt Trigger Inverter IC.
The Components You Need
| Part | Value | Note |
|---|---|---|
| – | Breadboard | Breadboard |
| – | Jumper Wires | Any stiff wire (22-23 AWG) |
| – | 9V Battery clip | To connect the battery to the board |
| BATT1 | 9V Battery | To power the circuit |
| U1 | 74C14 or CD40106 | Hex Schmitt Trigger Inverter |
| C1 | 100μF | Polarized capacitor |
| R1 | 10 kΩ | Any resistor type |
| R2 | 10 kΩ | Any resistor type |
| LED1 | Red | Standard LED (low power) |
These are pretty standard components that you can get from most places that sell parts for building electronics. I’ve created a page with a list of where to buy electronic components here. They’re also included in the Ohmify Beginner’s kit (except the battery).
Build Something Useful This Evening
This gadget lets you use any IR remote-control to control your lamp, garden lights, heater oven, garage door, or anything else.
Build The Circuit Step-by-Step
When you have the components in hand, you’re ready to build the circuit.
Not sure how the breadboard works? Then you might want to read How To Use a Breadboard first.
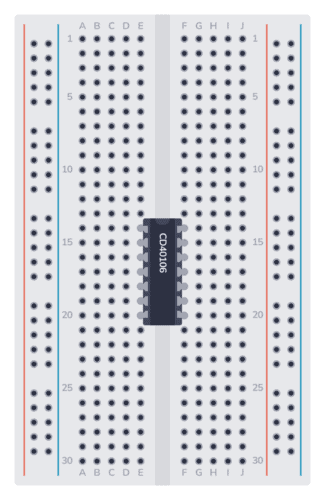
Step 1: Place the Integrated Circuit
Start with U1, the Hex Schmitt Trigger Inverter IC. Place it across the gap in the middle, with pin 1 in the upper left corner.
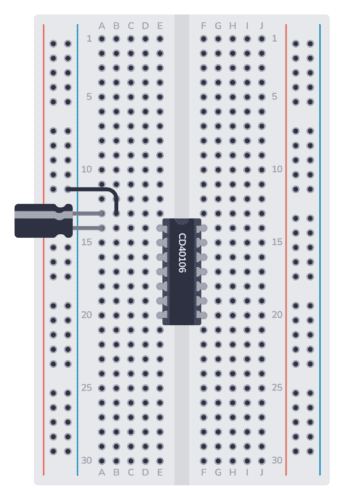
Step 2: Place the Capacitor (C1)
Next, place the capacitor C1. First, find the negative pin. It should be marked with a minus or zero. Often the negative pin is shorter than the positive pin. Connect the negative pin to the negative supply column (either directly or using a wire). And connect the positive pin to the same row as Pin 1 of the IC.
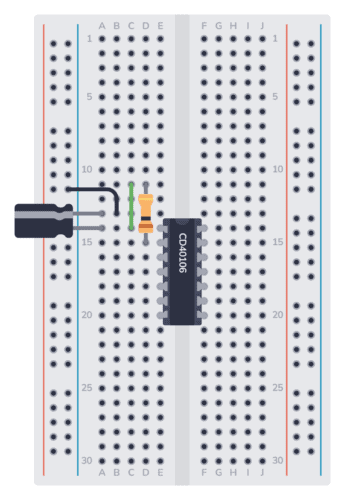
Step 3: Place the Resistor (R1)
Connect resistor R1. It should go from the input (Pin 1) to the output (Pin 2). Bend the legs of the resistor so that you can connect it from the row of Pin 1 to the row of Pin 2, or connect one side to an empty row and use a wire.
Step 4: Place the LED
Next, connect the LED. The negative leg of the LED is the shortest one. Connect it to the negative supply column (directly or using a wire). Connect the longer leg to an empty row.
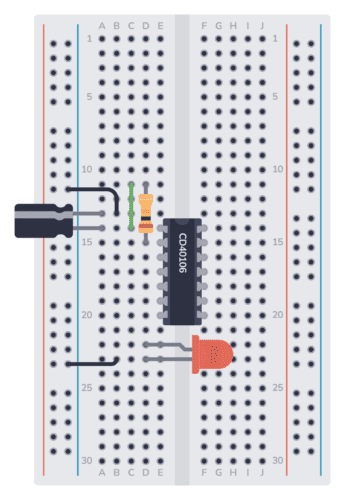
Step 5: Place the Resistor (R2)
The resistor R2 connects the output (Pin 2) to the LED. Place one leg of the resistor into the row of Pin 2. Place the other leg on the same row as the long leg of the LED.
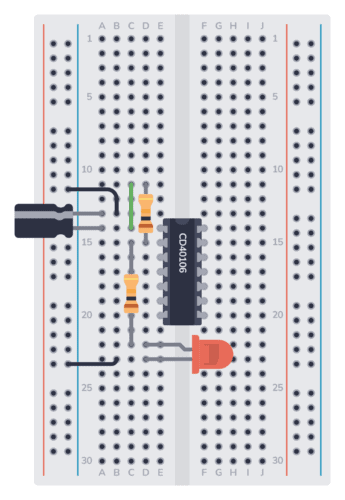
Step 6: Connect GND to Minus
The GND (Pin 7) of the IC must be connected to ground. In this circuit, ground is the minus of the battery. Connect one end of a jumper wire to the same row as Pin 7. Connect the other end to the negative supply column.
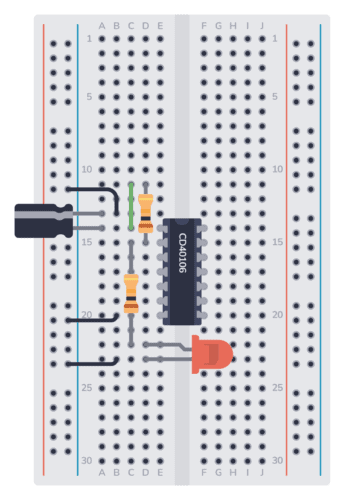
Step 7: Connect VDD to Plus
The VDD (Pin 14) of the IC must be connected to the positive supply. Connect one end of a jumper wire to the positive supply column. Connect the other end to the same row as Pin 14.
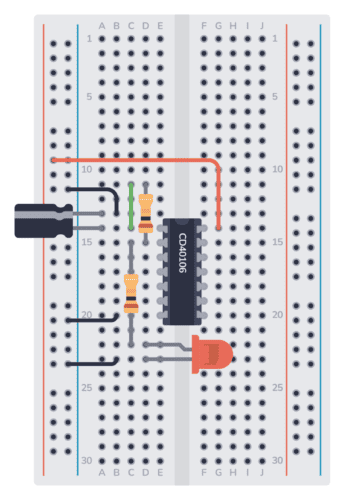
Step 8: Connect the Battery
Finally, connect the red wire from the battery to the positive supply column. And connect the black wire to the negative supply column.
Your LED should start to blink.
Questions?
Did you build it? How did it go?
Let me know in the comments below.
More Circuits & Projects Tutorials

Build Something Useful This Evening
This gadget lets you use any IR remote-control to control your lamp, garden lights, heater oven, garage door, or anything else.
